Setup Navigation¶
Set up your own location provider or use partner wrappers to enable indoor navigation in a plan.
Activate GPS/IPS option:¶
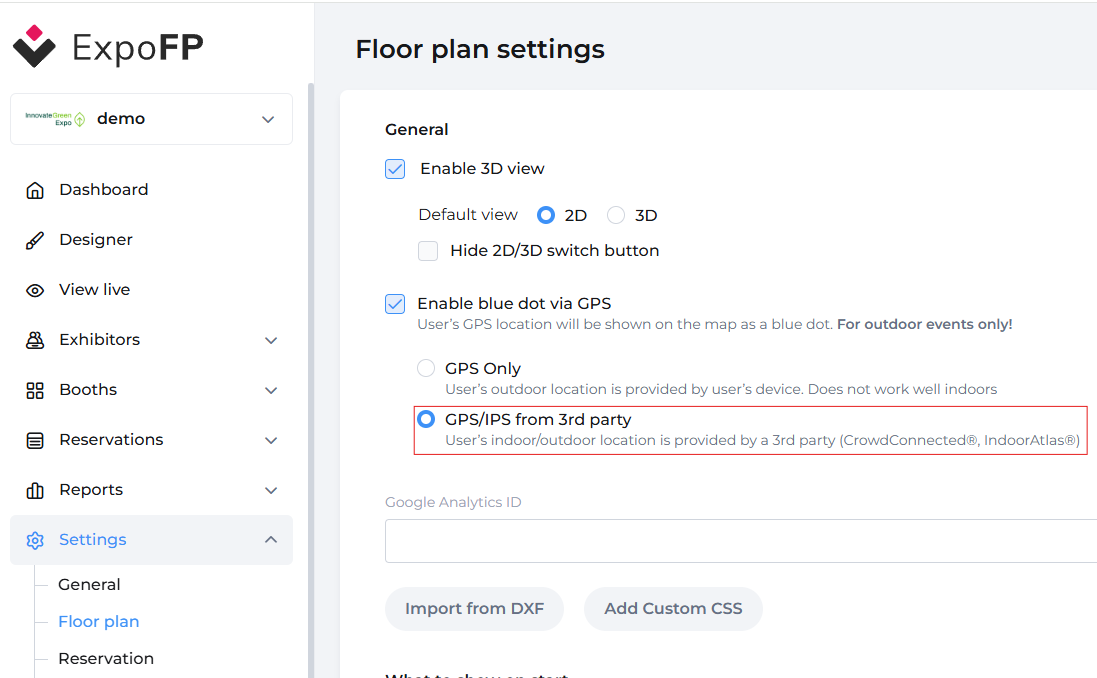
Recommended: Prefer coroutine-based APIs. Callback APIs are available for compatibility (e.g., Java).
Overview¶
- A plan consumes positions via
IExpoFpLocationProvider. - You can implement your own provider or use ExpoFP wrappers (CrowdConnected, IndoorAtlas).
- A provider may be attached to one presenter or shared as a global provider across screens.
Important: - When a plan appears, it calls
startUpdatingLocation()automatically. - When a plan disappears, it callsstopUpdatingLocation()only if the location provider is not global. - Any location provider error will be sent toplanStatusFlow.
Step 1. Add Dependencies (Gradle)¶
Use the 5.x line of ExpoFP artifacts. If you start from the latest 5.x release, pin to 5.3.4 ** (or 5.3.+ to receive only patch updates). You can also use 5.+** to stay on the latest 5.x.
Kotlin DSL (build.gradle.kts):
dependencies {
// Core ExpoFP SDK
implementation("com.expofp:fplan:5.3.4") // use actual version
// Partner wrappers (pick what you need)
implementation("com.expofp:crowdconnected:5.3.1") // CrowdConnected (foreground) - use actual version
implementation("com.expofp:crowdconnectedbackground:5.3.1") // CrowdConnected (background-capable) - use actual version
implementation("com.expofp:indooratlas:5.2.0") // IndoorAtlas - use actual version
}
Version Catalogs (gradle/libs.versions.toml):
[versions]
expofp = "use actual version"
[libraries]
expofp-fplan = { group = "com.expofp", name = "fplan", version.ref = "expofp" }
expofp-crowdconnected = { group = "com.expofp", name = "crowdconnected", version.ref = "expofp" }
expofp-crowdconnected-background = { group = "com.expofp", name = "crowdconnectedbackground", version.ref = "expofp" }
expofp-indooratlas = { group = "com.expofp", name = "indooratlas", version.ref = "expofp" }
Then use in build.gradle.kts:
dependencies {
implementation(libs.expofp.fplan)
implementation(libs.expofp.crowdconnected) // optional
implementation(libs.expofp.crowdconnected.background) // optional
implementation(libs.expofp.indooratlas) // optional
}
Step 2. Manifest Setup¶
Permissions depend on the provider (GPS, BLE beacons, IPS SDK). Include only what you actually use.
<manifest>
<!-- Network (map tiles, assets, etc.) -->
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE" />
<!-- Location -->
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION" />
<!-- Background location (optional; only if needed) -->
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_BACKGROUND_LOCATION" />
<!-- Bluetooth for IPS beacons (optional; Android 12+) -->
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH_SCAN" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH_CONNECT" />
<!-- Legacy Bluetooth (API < 31) -->
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH_ADMIN" />
<!-- Foreground service for location (if your provider runs a FGS) -->
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.FOREGROUND_SERVICE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.FOREGROUND_SERVICE_LOCATION" />
<!-- Notification permission for Android 13+ (required for FGS notification visibility) -->
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.POST_NOTIFICATIONS" />
<!-- Optional: BLE not strictly required -->
<uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.bluetooth_le" android:required="false" />
<application>
...
</application>
</manifest>
Step 3. Request Runtime Permissions (example)¶
For production, prefer the Activity Result API. Below is a minimal example for clarity.
val permsModern = arrayOf(
Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION,
Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION,
Manifest.permission.BLUETOOTH_SCAN,
Manifest.permission.BLUETOOTH_CONNECT
)
val permsLegacy = arrayOf(
Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION,
Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION
)
ActivityCompat.requestPermissions(
this,
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 31) permsModern else permsLegacy,
100
)
Step 4. Implement Your Own Provider¶
Implement IExpoFpLocationProvider and forward positions to the presenter through the delegate.
class YourLocationProvider(private val context: Context) : IExpoFpLocationProvider {
override var expoFpLocationProviderDelegate: ExpoFpLocationProviderDelegate? = null
private val fused by lazy { LocationServices.getFusedLocationProviderClient(context) }
private var callback: LocationCallback? = null
override var isLocationUpdating: Boolean = false
private set
@MainThread
override fun startUpdatingLocation() {
val request = LocationRequest.Builder(Priority.PRIORITY_HIGH_ACCURACY, 2000L).build()
callback = object : LocationCallback() {
override fun onLocationResult(result: LocationResult) {
val loc = result.lastLocation ?: return
val position = ExpoFpPosition(lat = loc.latitude, lng = loc.longitude)
expoFpLocationProviderDelegate?.positionDidChange(position)
}
}
try {
fused.requestLocationUpdates(request, callback as LocationCallback, Looper.getMainLooper())
isLocationUpdating = true
} catch (e: Exception) {
expoFpLocationProviderDelegate?.errorOccurred(
ExpoFpError.LocationProviderError(e.message ?: "Unknown error"),
ExpoFpLocationProviderType.Custom
)
}
}
override fun stopUpdatingLocation() {
callback?.let { fused.removeLocationUpdates(it) }
callback = null
isLocationUpdating = false
}
}
You can also use partner wrappers (CrowdConnected, IndoorAtlas) via ExpoFP modules. See below.
Step 5. Attach to Presenter¶
During presenter creation (recommended)¶
val locationProvider = YourLocationProvider(context)
val presenter = ExpoFpPlan.createPlanPresenter(
planLink = ExpoFpLinkType.ExpoKey("YourExpoKey"),
locationProvider = locationProvider
)
After presenter creation¶
presenter.setLocationProvider(YourLocationProvider(context))
When the plan view appears, the presenter calls
startUpdatingLocation()automatically. When the plan view disappears, it callsstopUpdatingLocation()only if the provider is not global.Any location provider error will be sent to
planStatusFlow.
Manual control remains available:
locationProvider.startUpdatingLocation()
locationProvider.stopUpdatingLocation()
Step 6. Global Location Provider¶
Use one provider instance across multiple plans.
// Set once
val provider = YourLocationProvider(context)
ExpoFpPlan.globalLocationProvider.sharedProvider = provider
// Optional manual control
ExpoFpPlan.globalLocationProvider.startUpdatingLocation()
// ...
ExpoFpPlan.globalLocationProvider.stopUpdatingLocation()
Attach global provider to a presenter:
val presenter = ExpoFpPlan.createPlanPresenter(
planLink = ExpoFpLinkType.ExpoKey("YourExpoKey"),
locationProvider = ExpoFpPlan.globalLocationProvider
)
// or later:
presenter.setLocationProvider(ExpoFpPlan.globalLocationProvider)
For global providers the presenter does not stop updates on view disappearance — manage lifecycle yourself.
Step 7. Listen to Location Updates Manually¶
When a presenter uses a provider, it sets itself as the provider's delegate.
If you set your own delegate, forward updates to the plan manually viaselectCurrentPosition(position, focus).
class YourLocationProviderDelegate(
private val presenter: IExpoFpPlanPresenter
) : ExpoFpLocationProviderDelegate {
@MainThread
override fun positionDidChange(newPosition: ExpoFpPosition) {
presenter.selectCurrentPosition(newPosition, focus = false)
}
}
Attach the delegate:
val provider = YourLocationProvider(context)
provider.expoFpLocationProviderDelegate = YourLocationProviderDelegate(presenter)
// For global provider:
// ExpoFpPlan.globalLocationProvider.expoFpLocationProviderDelegate = YourLocationProviderDelegate(presenter)
CrowdConnected (ExpoFP Wrapper)¶
Settings¶
val ccSettings = ExpoFpCrowdConnectedLocationProviderSettings(
appKey = "YOUR_APP_KEY",
token = "YOUR_TOKEN",
secret = "YOUR_SECRET",
navigationType = ExpoFpCrowdConnectedNavigationType.IPS, // or GEO / ALL
isAllowedInBackground = false, // true -> include ACCESS_BACKGROUND_LOCATION in checks
isHeadingEnabled = true, // enable azimuth heading
aliases = mapOf("visitorId" to "12345"),
notificationText = "Indoor navigation is active", // foreground service notification
serviceIcon = R.drawable.ic_navigation // notification icon
)
Build Warnings: When using CrowdConnected, manifest merge may show warnings about foreground service types on Android 14+. These are expected — the CrowdConnected SDK handles them internally.
Choose a Provider Class¶
// Foreground-only
val ccProvider = ExpoFpCrowdConnectedLocationProvider(applicationContext, ccSettings)
// Background-capable (adds BackgroundModule and background permission flow)
val ccBgProvider = ExpoFpCrowdConnectedBackgroundLocationProvider(applicationContext, ccSettings)
Start with Auto-Permissions¶
Activity vs RegistryOwner - Use
activityfor a simple Activity-based flow. - UseregistryOwnerwhen you integrate withActivityResultRegistry(common inside Compose and custom components).
> You can pass both when available.
Coroutine + Activity
lifecycleScope.launch {
ccProvider.startWithAutoPermissions(
owner = this@YourActivity, // LifecycleOwner
activity = this@YourActivity // Activity
)
}
Coroutine + ActivityResultRegistryOwner
lifecycleScope.launch {
ccProvider.startWithAutoPermissions(
owner = this@YourActivity, // LifecycleOwner
registryOwner = this@YourActivity // ActivityResultRegistryOwner
)
}
Callback + Activity
ccProvider.startWithAutoPermissions(
owner = this,
activity = this,
onStarted = { /* ready */ },
onDenied = { denied, permanentlyDenied -> /* handle */ },
onError = { e -> /* log */ }
)
Callback + ActivityResultRegistryOwner
ccProvider.startWithAutoPermissions(
owner = this,
registryOwner = this,
onStarted = { /* ready */ },
onDenied = { denied -> /* handle */ },
onError = { e -> /* log */ }
)
Attach to Presenter¶
presenter.setLocationProvider(ccProvider) // or ccBgProvider
Use Global Provider (Start Provider Early)¶
Start the provider before creating any map. The presenter won't block waiting for CC SDK — the blue dot appears when ready.
// 1. Register and start provider early
val ccProvider = ExpoFpCrowdConnectedLocationProvider(applicationContext, ccSettings)
ExpoFpPlan.globalLocationProvider.sharedProvider = ccProvider
lifecycleScope.launch {
ccProvider.startWithAutoPermissions(owner = activity, registryOwner = activity)
}
// 2. Create presenter anytime — doesn't wait for CC SDK
val presenter = ExpoFpPlan.createPlanPresenter(
planLink = ExpoFpLinkType.ExpoKey("YourExpoKey")
// locationProvider defaults to globalLocationProvider
)
// 3. Stop when leaving the app
ExpoFpPlan.globalLocationProvider.sharedProvider?.stopUpdatingLocation()
ExpoFpPlan.globalLocationProvider.sharedProvider = null
Note: For global providers, the plan does not call
stopUpdatingLocation()when the map closes.
Use in Compose¶
setContent {
val context = LocalContext.current
val activity = context as ComponentActivity
val scope = rememberCoroutineScope()
val expoView = remember { ExpoFpView(context).apply { attachPresenter(presenter) } }
Column {
Button(onClick = {
scope.launch {
ccProvider.startWithAutoPermissions(
owner = activity,
registryOwner = activity
)
}
}) { Text("Start navigation") }
AndroidView(factory = { expoView }, modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize())
}
}
Stop and Dispose¶
ccProvider.stopUpdatingLocation()
ccProvider.close()
Minimal example for provider.startWithAutoPermissions¶
class MainActivity : ComponentActivity() {
private lateinit var settings: ExpoFpCrowdConnectedLocationProviderSettings
private lateinit var provider: ExpoFpCrowdConnectedLocationProvider
private lateinit var presenter: IExpoFpPlanPresenter
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
ExpoFpPlan.initialize(this)
settings = ExpoFpCrowdConnectedLocationProviderSettings(
appKey = "YOUR_APP_KEY",
token = "YOUR_TOKEN",
secret = "YOUR_SECRET",
navigationType = ExpoFpCrowdConnectedNavigationType.ALL
)
provider = ExpoFpCrowdConnectedLocationProvider(
appContext = applicationContext,
settings = settings
)
presenter = ExpoFpPlan.createPlanPresenter(
planLink = ExpoFpLinkType.ExpoKey("demo")
)
lifecycleScope.launch {
try {
provider.startWithAutoPermissions(
owner = this@MainActivity,
registryOwner = this@MainActivity,
onDenied = { list -> Log.i("ExpoTest", "denied $list") },
onError = { e -> Log.e("ExpoTest", "perm/start error", e) }
)
presenter.setLocationProvider(provider)
} catch (t: Throwable) {
Log.e("ExpoTest", "Permissions flow failed", t)
}
}
setContent {
ExpoFpCrowdConnectedTheme {
DemoScreen(presenter = presenter)
}
}
}
override fun onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy()
provider.stopUpdatingLocation()
}
}
@Composable
private fun DemoScreen(
presenter: IExpoFpPlanPresenter
) {
val context = LocalContext.current
val expoView = remember { ExpoFpView(context).apply { attachPresenter(presenter) } }
Box(modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize()) {
AndroidView(factory = { expoView }, modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize())
}
}
IndoorAtlas (ExpoFP Wrapper)¶
Create Provider¶
val iaProvider = ExpoFpIndoorAtlasLocationProvider(
appContext = applicationContext,
apiKey = "YOUR_IA_API_KEY",
apiSecret = "YOUR_IA_API_SECRET"
)
Start with Auto-Permissions¶
Activity vs RegistryOwner — same rationale as above.
Coroutine + Activity
lifecycleScope.launch {
iaProvider.startWithAutoPermissions(
owner = this@YourActivity,
activity = this@YourActivity
)
}
Coroutine + ActivityResultRegistryOwner
lifecycleScope.launch {
iaProvider.startWithAutoPermissions(
owner = this@YourActivity,
registryOwner = this@YourActivity
)
}
Callback + Activity
iaProvider.startWithAutoPermissions(
owner = this,
activity = this,
onStarted = { /* ready */ },
onDenied = { denied, permanentlyDenied -> /* handle */ },
onError = { e -> /* log */ }
)
Callback + ActivityResultRegistryOwner
iaProvider.startWithAutoPermissions(
owner = this,
registryOwner = this,
onStarted = { /* ready */ },
onDenied = { denied -> /* handle */ },
onError = { e -> /* log */ }
)
Attach to Presenter¶
presenter.setLocationProvider(iaProvider)
Use in Compose¶
setContent {
val context = LocalContext.current
val activity = context as ComponentActivity
val scope = rememberCoroutineScope()
val expoView = remember { ExpoFpView(context).apply { attachPresenter(presenter) } }
Column {
Button(onClick = {
scope.launch {
iaProvider.startWithAutoPermissions(
owner = activity,
registryOwner = activity
)
}
}) { Text("Start navigation") }
AndroidView(factory = { expoView }, modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize())
}
}
Stop and Dispose¶
iaProvider.stopUpdatingLocation()
iaProvider.close()
Best Practices¶
- Request only needed permissions: tailor to your provider (GPS/BLE/IPS).
- Prefer coroutine APIs for lifecycle-aware control.
- Explain background location to users and keep a persistent notification for foreground service.
- Use a global provider only if several screens share the same location stream.
- Stop updates when not needed to save battery.
- Do not block the main thread inside provider callbacks; offload heavy work to coroutines.